Are you an investor seeking to minimize your tax liability and maximize your investment returns? This article explores smart tax strategies specifically designed for investors, covering topics such as tax-efficient investing, capital gains tax optimization, and tax loss harvesting. Learn how to strategically leverage various tax deductions and credits to legally reduce your tax burden and keep more of your hard-earned investment profits. Discover effective strategies to navigate the complexities of tax planning for investments and achieve your financial goals with greater efficiency.
How Taxes Affect Investment Returns
Taxes significantly impact your investment returns. The type of investment you choose determines the tax implications. For example, capital gains taxes apply to profits from selling stocks or bonds, while dividends are taxed as ordinary income for many investors. Interest income from bonds is also typically taxable.
Your tax bracket plays a crucial role. Higher earners face higher tax rates, thus reducing their net investment returns. Tax-advantaged accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, offer ways to defer or reduce taxes on investment growth, ultimately boosting your after-tax returns. However, even within these accounts, there can be rules and tax implications depending on the type of account and withdrawal strategy.
Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy used to offset capital gains with capital losses, reducing your overall tax liability and increasing your net returns. Understanding tax rates, brackets, and applicable rules allows investors to develop strategies for minimizing tax burdens and maximizing investment gains. Careful planning and professional advice can significantly improve your investment outcomes.
Tax-Advantaged Investment Accounts
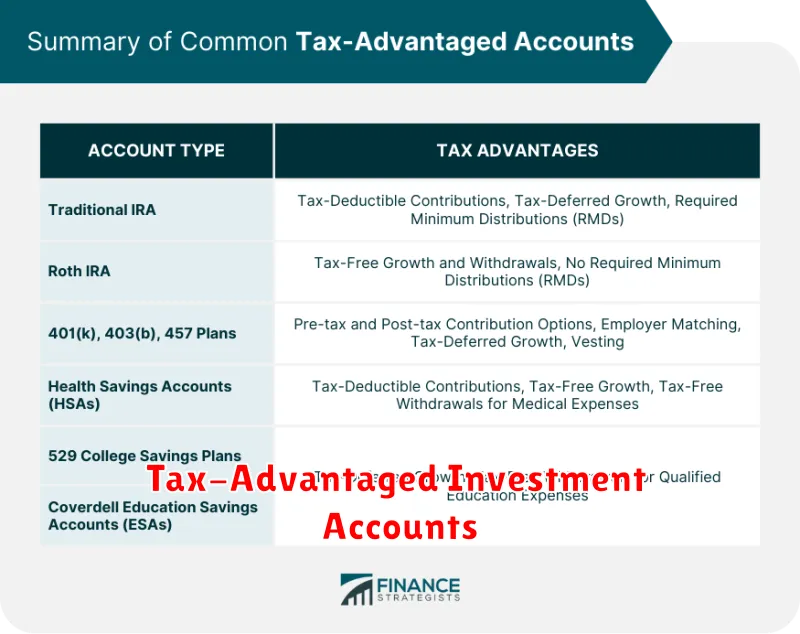
Tax-advantaged investment accounts offer significant benefits for investors seeking to minimize their tax burden and maximize investment growth. These accounts allow for tax-deferred or tax-free growth, depending on the specific type of account.
Retirement accounts such as 401(k)s and Traditional IRAs provide tax deferral, meaning taxes are only paid upon withdrawal in retirement. Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s offer tax-free growth and withdrawals in retirement, provided certain conditions are met. Contributions to Roth accounts are made after tax, but qualified withdrawals are tax-free.
Health savings accounts (HSAs) are another valuable option, allowing for tax-deductible contributions to cover medical expenses. The funds grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are also tax-free.
Choosing the right tax-advantaged account depends on individual circumstances, including income level, investment timeline, and risk tolerance. Careful planning is crucial to optimize tax efficiency and maximize long-term investment returns.
How to Minimize Capital Gains Taxes

Capital gains taxes can significantly reduce your investment returns. Fortunately, several strategies can help minimize your tax liability. Understanding these strategies is crucial for maximizing your after-tax profits.
One key strategy is tax-loss harvesting. This involves selling losing investments to offset gains, reducing your overall taxable income. It’s important to note that you can only deduct up to $3,000 ($1,500 if married filing separately) in capital losses annually against ordinary income; exceeding this amount carries over to future years.
Strategic asset allocation plays a vital role. Diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes can help mitigate risk and potentially lower your exposure to capital gains taxes in any given year. This doesn’t eliminate taxes, but spreads them out, potentially keeping your tax bracket lower.
Long-term capital gains rates are generally lower than short-term rates. Holding investments for at least one year and one day qualifies them for the lower long-term rates. This simple strategy can have a substantial impact on the total tax you owe.
Gifting appreciated assets to loved ones can help reduce your estate tax liability. This involves transferring assets before death and utilizing annual gift tax exclusions to avoid tax implications on the transferred asset’s value. However, this must be done strategically and in compliance with relevant gift and estate tax laws. Consult a tax professional for personalized guidance on this method.
Qualified dividends are taxed at the same rates as long-term capital gains, making dividend-paying stocks an attractive option for long-term investors seeking to potentially lower their tax burden. However, dividend taxation still applies.
Finally, consulting a tax professional is strongly recommended. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific financial situation and help you develop a comprehensive tax-minimization strategy. Remember that tax laws are complex and subject to change; professional guidance is invaluable.
The Importance of Tax-Loss Harvesting

Tax-loss harvesting is a powerful strategy for investors to reduce their tax liability. It involves selling investments that have lost value to offset capital gains from other investments.
By strategically realizing losses, investors can lower their taxable income, resulting in significant tax savings. This allows for more capital to remain invested and potentially grow over time.
The maximum annual loss that can be used to offset ordinary income is $3,000 ($1,500 if married filing separately). Any excess losses can be carried forward to future years.
Careful planning is crucial for successful tax-loss harvesting. Investors should consult with a qualified financial advisor to determine the best approach for their individual circumstances and investment portfolio.
Timing is also key. Tax-loss harvesting is most effective when done strategically near the end of the tax year. However, it’s important to consider the wash-sale rule, which prevents investors from repurchasing substantially identical securities within 30 days of the sale.
Understanding Dividend Taxation

Understanding how dividends are taxed is crucial for investors. Dividends, payments made by a company to its shareholders from its profits, are considered taxable income in the US. The tax rate depends on your tax bracket and the type of dividend received – qualified or non-qualified.
Qualified dividends, generally from US corporations held for a specific period, receive a preferential tax rate. This rate is typically lower than your ordinary income tax rate. Non-qualified dividends, which might include dividends from certain foreign corporations or those held for a shorter period, are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate.
The tax form used to report dividend income is Form 1099-DIV, which you receive from the payer. Accurate record-keeping of your dividend income is essential for accurate tax filing. Consulting with a tax professional can help navigate the complexities of dividend taxation and ensure you’re taking advantage of all applicable tax benefits.
The Role of Municipal Bonds in Tax Planning

Municipal bonds, issued by state and local governments to finance public projects, offer a significant advantage for investors seeking to reduce their tax burden. A key feature is their tax-exempt status on the interest income for federal income tax purposes. This means that the interest earned is not subject to federal taxes, resulting in a higher net return compared to taxable bonds with similar risk profiles.
However, it’s crucial to understand that tax-exemption can vary. While interest is typically exempt from federal taxes, it may be subject to state and local taxes depending on the issuer and the investor’s residence. Investors residing in the state where the bonds were issued often enjoy a double tax advantage: exemption from both federal and state taxes. Carefully consider your state’s tax laws before investing.
The tax benefits of municipal bonds are most appealing to investors in higher tax brackets. The higher the tax bracket, the greater the potential savings from the tax-exempt interest. This makes them a particularly valuable tool for strategic tax planning in retirement portfolios, where maximizing after-tax returns is paramount.
It is important to note that while municipal bonds offer tax advantages, they also carry investment risks. Like all bonds, their value can fluctuate based on market interest rates and the creditworthiness of the issuer. Diversification within a portfolio is crucial to mitigate these risks.
Tax Strategies for Retirement Savings

Strategic tax planning is crucial for maximizing your retirement savings. Understanding and utilizing available tax advantages can significantly boost your retirement nest egg.
Tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and Traditional IRAs, allow for pre-tax contributions, reducing your current taxable income. However, withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income. Roth IRAs offer a different approach; contributions are made after tax, but withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, providing a significant long-term benefit.
Tax-loss harvesting can be a powerful tool. If you have investment losses, offsetting them against capital gains can reduce your tax liability. Careful planning allows you to strategically utilize losses to minimize your tax burden while maintaining your overall investment strategy.
Consider your income bracket. Higher earners may find that Roth contributions are less advantageous due to the upfront tax burden, while lower earners might benefit greatly from the tax-free withdrawals in retirement. Consult with a financial advisor to determine the best strategy for your specific circumstances.
Diversification across various tax-advantaged accounts can create a balanced and efficient retirement savings strategy, further minimizing your tax liability throughout your lifetime.
Professional advice is recommended. A financial advisor or tax professional can help you navigate the complexities of tax laws and create a personalized plan that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Avoiding Tax Penalties on Investments

Understanding tax implications is crucial for successful investing. Failing to meet tax deadlines or inaccurately reporting investment income can lead to significant penalties. These penalties can include interest charges on unpaid taxes and potentially additional fines depending on the severity and nature of the violation.
To avoid penalties, maintain meticulous records of all investment transactions, including purchase dates, costs, and sales proceeds. Utilize tax software or consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate reporting. Familiarize yourself with the relevant tax laws and regulations pertaining to your specific investments, such as capital gains taxes, dividends, and interest income.
Timely filing of tax returns is paramount. Missing deadlines can result in automatic penalties. If you anticipate difficulty meeting a deadline, consider filing an extension to avoid penalties, though you’ll still need to pay any taxes owed by the original deadline. Furthermore, proactively addressing any discrepancies or issues with your tax return will reduce the likelihood of penalties. Seeking professional advice is recommended for complex investment portfolios.
By diligently tracking investments, accurately reporting income, and filing tax returns on time, investors can significantly reduce the risk of incurring penalties and maintain a healthy financial standing.

