Building a diversified investment portfolio is crucial for long-term financial success. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps of creating a portfolio that aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. Learn how to strategically allocate assets across various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments, to minimize risk and maximize potential returns. We’ll explore effective diversification strategies, portfolio rebalancing techniques, and the importance of regular review and adjustment to ensure your investments remain aligned with your evolving needs. Discover how to build a robust and resilient investment portfolio that can weather market volatility and help you achieve your financial aspirations.
What is Portfolio Diversification?
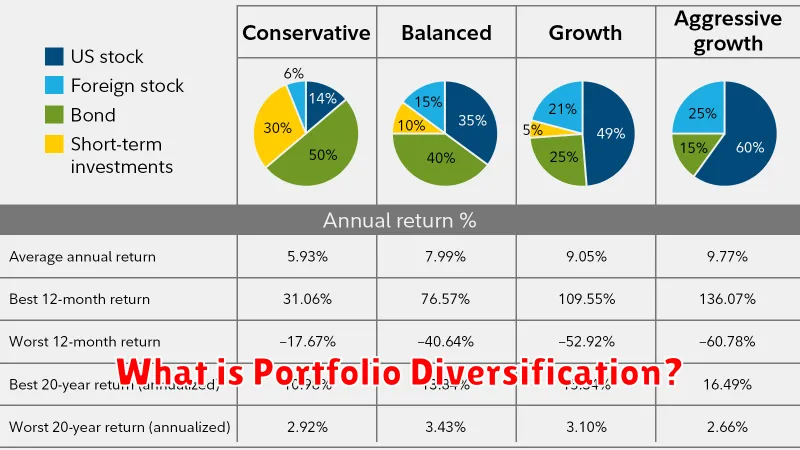
Portfolio diversification is a risk management strategy that involves spreading investments across a variety of asset classes, sectors, and geographies. This approach aims to reduce the overall risk of the portfolio by mitigating the impact of poor performance in any single investment.
Instead of concentrating holdings in a few areas, diversification involves allocating capital to a range of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. This reduces the reliance on any one asset’s performance to determine the overall portfolio success.
The core principle is that uncorrelated assets, meaning those that do not move in tandem, will offset each other’s fluctuations. When one investment underperforms, others may perform well, leading to a more stable overall portfolio value.
Effective diversification is not simply about owning many different investments; it’s about carefully selecting assets that offer the desired balance of risk and return. The optimal level of diversification varies depending on individual investor goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Why Diversification Reduces Risk

Diversification is a fundamental investment strategy that reduces risk by spreading investments across various asset classes. This means instead of putting all your eggs in one basket (e.g., only investing in stocks), you distribute your capital across different assets like stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
The core principle is that the performance of different asset classes often doesn’t move in perfect correlation. When one investment performs poorly, another may perform well, or at least not decline as sharply. This offsetting effect lessens the overall volatility of your portfolio and reduces the likelihood of significant losses.
Reduced Volatility: Diversification dampens the impact of market fluctuations. A diversified portfolio tends to experience smaller swings in value compared to a concentrated portfolio.
Lower Probability of Total Loss: By spreading your investments, the risk of losing your entire investment due to a single catastrophic event affecting a specific asset class is greatly reduced.
Improved Risk-Adjusted Returns: While diversification doesn’t guarantee higher returns, it can potentially improve your risk-adjusted returns, meaning you achieve a comparable return with significantly less volatility.
Important Note: Diversification is not a guarantee against losses. Market downturns can still impact the overall value of your portfolio. However, a well-diversified portfolio is better positioned to weather these storms.
How to Balance Stocks, Bonds, and Real Estate

Balancing your investment portfolio across stocks, bonds, and real estate is crucial for diversification and mitigating risk. The ideal allocation depends on your risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer.
Stocks offer higher potential returns but greater volatility. They are suitable for investors with a longer time horizon and a higher risk tolerance. Bonds, on the other hand, provide relatively lower returns but greater stability, making them ideal for preserving capital and reducing risk. They are generally preferred by investors with shorter time horizons or lower risk tolerance.
Real estate can offer diversification benefits, providing a hedge against inflation and potentially generating rental income. However, it’s typically less liquid than stocks and bonds, meaning it can be harder to quickly convert into cash. Real estate investments also often require significant upfront capital and ongoing maintenance costs.
A common approach is a 60/40 portfolio, allocating 60% to stocks and 40% to bonds. However, incorporating real estate would alter this ratio. A sample allocation could be 50% stocks, 30% bonds, and 20% real estate. Adjustments should be made based on individual circumstances. Consider consulting with a financial advisor for personalized guidance.
Remember, diversification doesn’t eliminate risk but rather helps to manage it. Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure it aligns with your evolving financial goals and risk tolerance.
International Investments: Should You Go Global?

Diversification is a cornerstone of a robust investment strategy, and incorporating international investments can significantly enhance your portfolio’s resilience. Global diversification reduces your reliance on a single country’s economic performance, mitigating risk associated with regional downturns or political instability.
However, international investing also presents challenges. Currency fluctuations can impact returns, and navigating different regulatory environments and market complexities requires careful consideration. Research and due diligence are crucial before investing in foreign markets.
The decision of whether to go global depends on your risk tolerance, investment timeline, and overall financial goals. A longer time horizon generally offers greater opportunity to weather short-term market volatility. Consult with a financial advisor to determine the optimal allocation of your assets between domestic and international investments.
Benefits of international diversification can include access to higher growth potential in emerging markets, exposure to a wider range of investment opportunities, and potentially better risk-adjusted returns over the long term. However, it is important to remember that higher potential returns often come with higher risk.
Ultimately, the choice is a personal one, requiring careful assessment of your individual circumstances and investment objectives. A balanced approach, incorporating both domestic and international assets, can be an effective way to achieve diversification and manage risk within your portfolio.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio for Long-Term Growth

Rebalancing your investment portfolio is a crucial strategy for long-term growth. It involves periodically adjusting your asset allocation to maintain your target percentages across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate.
Over time, some investments will outperform others, causing your portfolio to drift from its original allocation. Rebalancing involves selling some of your better-performing assets and buying more of those that have underperformed, bringing your portfolio back to its target allocation.
This disciplined approach offers several key benefits. It helps you capitalize on market fluctuations by buying low and selling high (relatively speaking). It also reduces risk by preventing overexposure to any single asset class, thereby promoting a more stable and resilient portfolio over the long term.
The frequency of rebalancing depends on your individual investment goals and risk tolerance. Some investors rebalance annually, while others do it semi-annually or even quarterly. A consistent approach is vital for effective rebalancing.
While rebalancing involves transaction costs, these costs are generally outweighed by the long-term benefits of maintaining a well-diversified and balanced portfolio. It’s a key element of a successful long-term investment strategy.
How to Use ETFs for Diversification
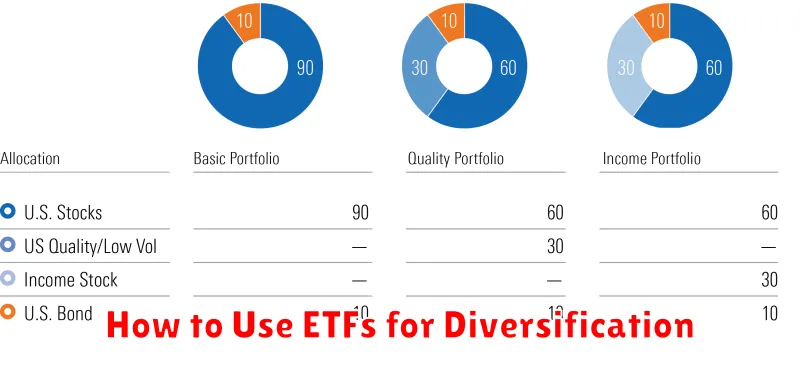
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) offer a powerful tool for achieving diversification within your investment portfolio. Unlike individual stocks, which carry significant risk, ETFs allow you to invest in a basket of assets, instantly diversifying your holdings across various sectors, geographies, or asset classes.
To effectively use ETFs for diversification, consider your investment goals and risk tolerance. Then, select ETFs that align with your strategy. For example, a broad market ETF like one tracking the S&P 500 provides instant diversification across large-cap U.S. companies. Alternatively, you could choose sector-specific ETFs (e.g., technology, healthcare) or international ETFs to further diversify geographically.
Asset allocation is key. Determine the percentage of your portfolio you want to allocate to different asset classes (e.g., stocks, bonds, real estate) and select ETFs accordingly. A well-diversified portfolio usually incorporates a mix of asset classes to mitigate risk. Remember to regularly rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation as market conditions change.
Consider using ETFs that track different market capitalization ranges (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap) for broader market exposure. Also, explore ETFs focused on specific investment themes or factors (e.g., sustainable investing, value investing) to fine-tune your diversification strategy. Always conduct thorough research before investing in any ETF and understand the fund’s expense ratio and investment objectives.
By strategically employing ETFs, you can build a more resilient and diversified investment portfolio, potentially reducing overall risk and enhancing your long-term investment returns. Remember, diversification does not guarantee profits but aims to reduce the impact of potential losses in any single investment.
Investing in Alternative Assets
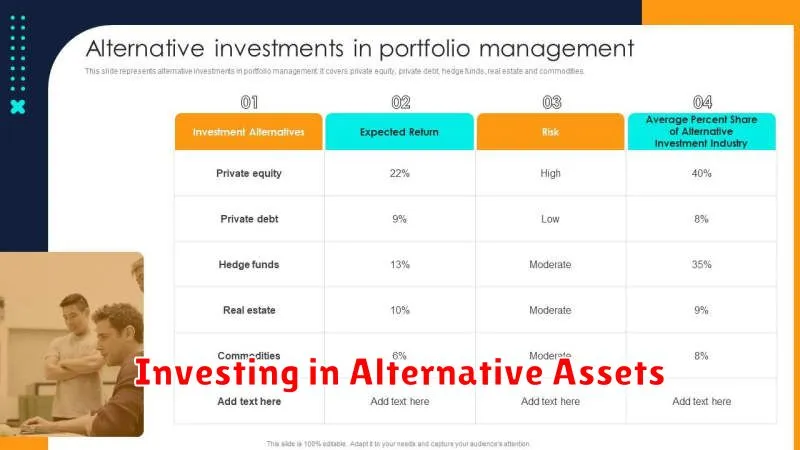
Diversification is key to mitigating risk in any investment portfolio. While traditional assets like stocks and bonds form the foundation, incorporating alternative assets can significantly enhance returns and reduce overall portfolio volatility.
Alternative assets encompass a broad range of investments outside of traditional markets. This includes real estate, offering potential for rental income and appreciation; private equity, providing exposure to high-growth companies; hedge funds, employing complex strategies to generate returns in various market conditions; commodities like gold and oil, acting as inflation hedges; and collectibles, such as art or rare stamps, that may appreciate over time.
Investing in alternative assets requires careful consideration. They often have higher minimum investment requirements, lower liquidity, and potentially higher fees than traditional investments. Due diligence, understanding associated risks, and seeking professional advice are crucial before allocating capital to these asset classes. Proper diversification within the alternative asset category itself is also recommended.
Remember that while alternative assets offer diversification benefits, they shouldn’t replace a well-structured core portfolio of stocks and bonds. The optimal allocation to alternative assets depends on individual risk tolerance, investment goals, and overall financial situation.
Common Portfolio Diversification Mistakes

One common mistake is over-diversification. While diversification is crucial, holding too many investments can dilute returns and increase management complexity. Focus on a manageable number of well-researched assets across different asset classes.
Another mistake is under-diversification or concentration risk. Over-reliance on a single asset class, sector, or company exposes your portfolio to significant losses if that specific area underperforms. Proper diversification requires spreading your investments across various uncorrelated assets.
Ignoring asset allocation is a critical error. A well-defined asset allocation strategy, tailored to your risk tolerance and financial goals, is essential for long-term success. Failing to regularly rebalance your portfolio to maintain your target allocation can significantly impact your returns.
Ignoring correlation is also common. Diversification doesn’t simply mean owning many things; it means owning assets that move independently of each other. Investing in highly correlated assets reduces the effectiveness of diversification, as they tend to rise and fall together.
Finally, failing to regularly review and adjust your portfolio based on your evolving financial situation and market conditions is a significant oversight. Market fluctuations and personal circumstances require periodic adjustments to your investment strategy.

